What Are ReactiveSearch Scripts
A script is a user defined JavaScript function typically executed during the request or response cycle of a search query or when indexing data. A script can also be invoked with a cron trigger. Scripts are available as an action with query rules.
Note: Conceptually, a script is run in a V8 engine isolate, and it is architecturally similar to how a Cloudflare worker operates.
Use-cases for scripts:
- Use a synchronous fetch request to get additional context, e.g. knowledge graph for a search query to return along with the search engine response
- Use an asynchronous fetch request to create a side-effect, e.g. saving search logs/state to an external system, recording of search analytics to an external system
- Use NLU/NLP to recognize entities and other PoS to modify the weights of the search query terms
- Use cryptographic utilities to apply additional security checks
Scripts run on the same machine that hosts the reactivesearch-api service (and Elasticsearch if it is hosted with appbase.io) and can make use of storage and state persistence using Elasticsearch.
Types of Scripts
We can categorize the scripts into two categories on the basis of execution context.
- Request
- Response
- Cron
Response scripts would have access to the request and envs which can be used to within the script. A Request script must return the request object.
Post-Request scripts would have access to the request, response and envs and expected to return the response object.
Cron scripts would be run at a certain schedule (passed during creation). It will have access to just the user passed envs.
Script context
Script has access to a global object named context (read only) that has the following properties:
request
cronscripts do not get this field.
It contains the request information, which has the following structure:
{
body: string,
headers: Object
}bodyrepresents the request body in string format.headersrepresents request headers in the key/value format, wherekeyrepresents the header name andvaluerepresents the header value.
response
cronscripts do not get this field.
Response returned by Elasticsearch in the following format:
{
code: number,
body: string,
headers: Object
}codeHTTP response status codebodyrepresents the response body in string format.headersrepresents response headers in the key/value format, wherekeyrepresents the header name andvaluerepresents the header value.
Note: The
responseproperty is not available in Pre-Request scripts.
envs
cronscripts do not get the following envs. It is passed theenvsthat the user sets while creating the cron script.
Environment variables specific to a request, which could be helpful to write conditional logic in a script. The envs object has the following properties:
{
index: Array<string>,
category: string,
acl: string,
origin: string,
referer: string,
ipv4: string,
ipv6: string,
query: string,
type: string,
customEvents: Object,
filters: Object,
}-
Environments available to all requests
indexrepresents the index used to query ElasticsearchcategoryCategories are analogous to the Elasticsearch API categories, like Cat API, Search API, Docs API and so on. You can check the categories at hereaclACLs adds another layer of granularity within each Elasticsearch API category. You can find the ACLs at hereoriginRequest origin, for e.g.https://my-search.domain.comrefererHTTP referer, e.g.https://my-search.domain.com/path?q=helloipv4IP address v4ipv6IP address v6
-
Environments specific to ReactiveSearch API
query: Value to be searched on, for e.giphonetype: Represents thetypeof request. Read morecustomEvents: Represents a map of custom events used in request.filters: Filters extracted from the request body oftermtype of requests, where -keyrepresents the filter name andvalueis the filter value.
An example with all environments
{
index: ["products"],
category: 'reactivesearch',
acl: 'reactivesearch',
origin: 'https://my-search.domain.com',
referer: 'https://my-search.domain.com/path?q=hello',
ipv4: '29.120.12.12',
ipv6: '2001:db8:3333:4444:5555:6666:7777:8888',
query: "sneakers",
type: "search",
customEvents: { platform: 'mac' },
filters: {"brand": "Puma"},
}How to define a script?
Request script
A request script can be used to modify the incoming request or perform a side effect (for e.g. send reports to analytics) before the final request is made to Elasticsearch.
request script must implement the following function:
function handleRequest() {
// do something here
return context.request
}Example
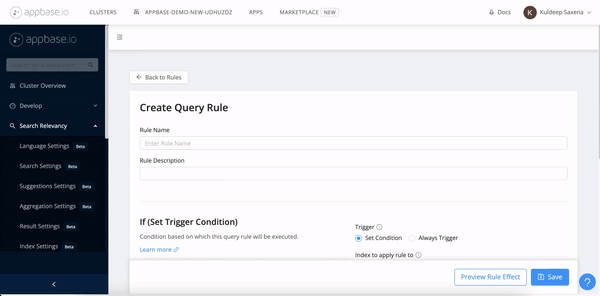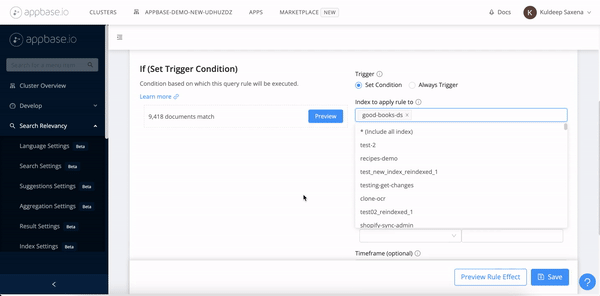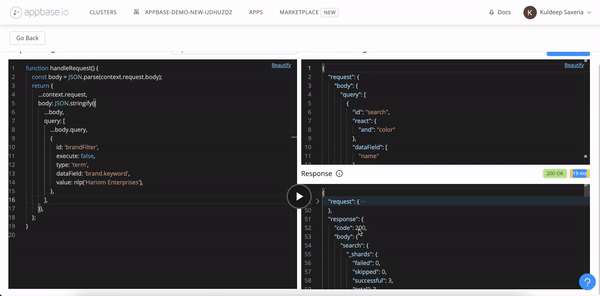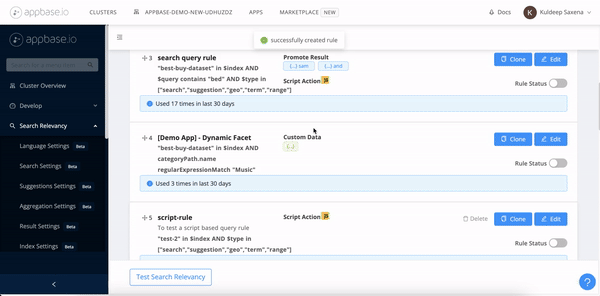
The following script modifies the request body by adding a filter by brand name.
function handleRequest() {
const requestBody = JSON.parse(context.request.body);
return {
...context.request,
body: JSON.stringify({
...requestBody,
query: [
...requestBody.query,
{
id: 'brandFilter',
execute: false,
type: 'term',
dataField: 'brand.keyword',
value: 'Appbase'
}
]
})
}
}Response script
Response script is useful to modify the Elasticsearch response or perform a side effect (for e.g. saved search) after getting the response from Elasticsearch.
Pre-request script must implement the following function:
function handleResponse() {
// do something here
return context.response
}The following script modifies the response body by adding a custom value in response.
function handleResponse() {
const responseBody = JSON.parse(context.response.body);
return {
...context.response,
body: JSON.stringify({
...responseBody,
custom_key: 'test'
})
}
}Cron Script
Cron scripts are useful to run a certain task with a schedule. For eg: thinnk of a script that fetches data from some external endpoint and adds it to a certain index every n minutes. Cron scripts allow to do that.
Unlike request and response scripts, cron scripts just take a block of code and runs it as a JS script. This gives the user more freedom regarding their code.
The following script adds a data to the test index.
The schedule should be passed in the trigger.expression field.
const data = {
'data': {
'my_data': true
}
};
async function putData() {
const r = await fetch('http://localhost:8000/test-v2/_doc', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': context.envs.auth
},
body: JSON.stringify(data)
});
}
putData();Validate Script
A script can be validated using the _script/validate endpoint. It is possible to validate a script with custom context variables (request, response and envs).
The following request modifies the request body, which can be seen in the response of the _script/validate route.
curl --location -g --request POST 'http://{{username}}:{{password}}@{{host}}/_script/validate' \
--data-raw '{
"request": {
"body": {
"query": [
{
"id": "search",
"react": {
"and": "brandFilter"
}
}
]
}
},
"script": "function handleRequest(){ const body = JSON.parse(context.request.body); return { ...context.request, body: JSON.stringify({...body, query: [...body.query, { id: `brandFilter`, execute: false, type: `term`, dataField: `brand.keyword`, value: nlp(`Microsoft top products`).topics().text() }] })} }",
"envs": {
"index": [
"test"
]
}
}'Create a Query rule with script
Query Rules are trigger events for the scripts. A rule can be defined with a script action and trigger condition.
The following request creates a rule with a script action to modify the request where index is products.
curl --location -g --request POST 'http://{{username}}:{{password}}@{{host}}/_rule' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"name": "my-rule",
"description": "To test query rule",
"trigger": {
"type": "filter",
"expression": "'\''products'\'' in $index"
},
"actions": [
{
"type": "script",
"script": "function handleRequest(){ const body = JSON.parse(context.request.body); return { ...context.request, body: JSON.stringify({...body, query: [...body.query, { id: `brandFilter`, execute: false, type: `term`, dataField: `brand.keyword`, value: nlp(`Microsoft top products`).topics().text() }] })} }"
}
]
}'You can check the endpoint details at here.
Create a script rule with Appbase.io Dashboard
The query rules GUI (Dashboard -> Search Relevancy -> Query Rules) can be used to define a rule with script action. You can start with a script template and extend it as per your business logic.